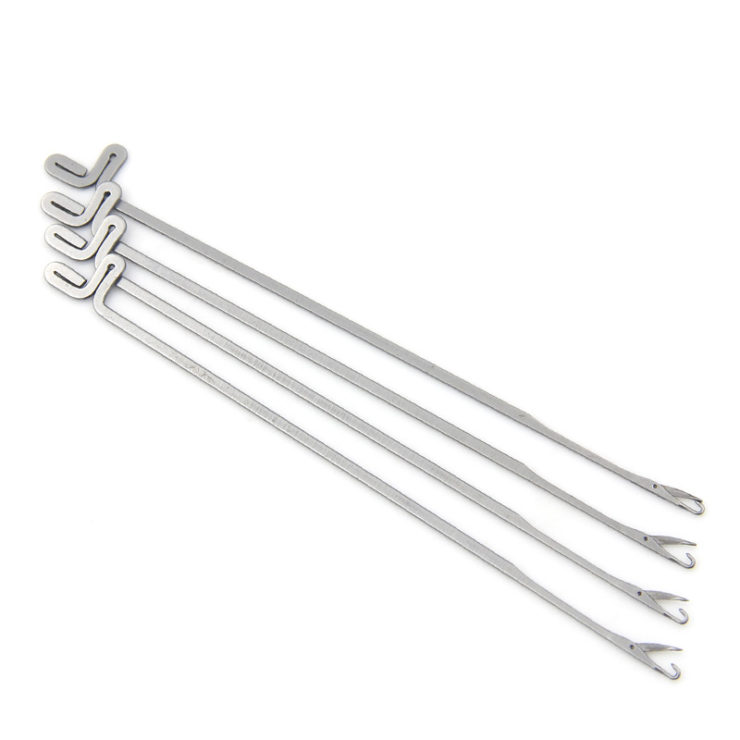
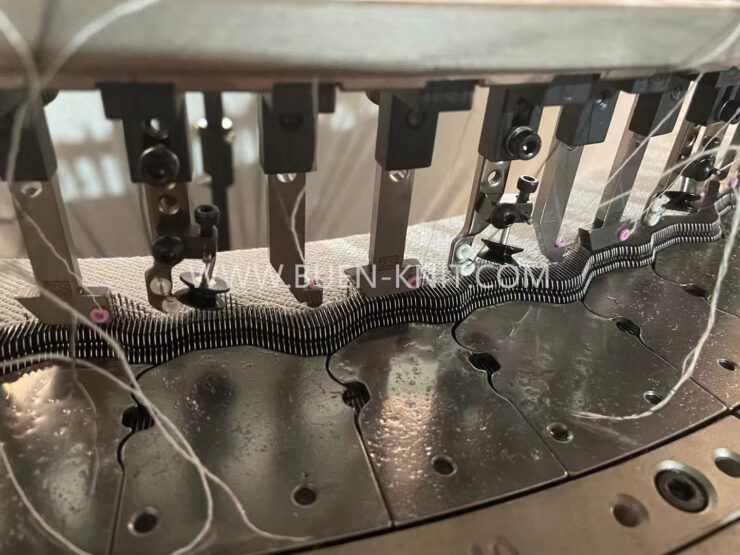
1 The rest position. The head of the needle hook is level with the top of the verge of the trick. The loop formed at the previous feeder is in the closed hook. It is prevented from rising as the needle rises, by holding-down sinkers or web holders that move forward between the needles to hold down the sinker loops.
2 Latch opening. As the needle butt passes up the incline of the clearing cam, the old loop, which is held down by the sinker, slides inside the hook and contacts the latch, turing and opening it.
3. Clearing height. When the needle reaches the top of the cam, the old loop is cleared from the hook and latch spoon on to the stem. At this point the feeder guide plate acts as a guard to prevent the latch from closing the empty hook.
4. Yarn feeding and latch closing. The needle starts to descend the stitch cam so that its latch is below the verge, with the old loop moving under it. At this point the new yarn is fed through a hole in the feeder guide to the descending needle hook, as there is no danger of the yarn being fed below the latch. The old loop contacts the underside of the latch, causing it to close on to the hook.
5. Knocking-over and loop length formation. As the head of the needle descends below the top of the trick, the old loop slides off the needle and the new loop is drawn through it. The continued descent of the needle draws the loop length, which is approximately twice the distance the head of the needle descends, below the surface of the sinker or trick-plated supporting the sinker loop.The distance is determined by the depth setting of the stitch cam, which can be adjusted.